Imagine a world where poetic verses flow effortlessly not from the depths of human emotion, but from the comprehensive data banks of an Artificial Intelligence (AI) system. Welcome to 2023! In today’s rapidly evolving literary landscape, AI poetry writing is revolutionizing the way we think about and experience the ancient art of poetry. As intricate as Shakespearean sonnets and as mesmerizing as Emily Dickinson’s verses, AI-generated poetry is leaving even the most avid lovers of verse in awe. Stick around with On-Page.ai to discover how artificial intelligence has stepped out from behind its tech curtain, ready to write its own magnum opus in poetic history – forever changing the way we engage with this timeless art form.

Artificial intelligence (AI) has been utilized to generate poetry with promising results. AI programs have been fed large datasets of existing poems, allowing them to generate their own original pieces. However, AI-generated poetry still faces challenges in terms of selecting winning poems and ensuring they adhere to various poetic constraints. The current state of AI-generated poetry is a benchmark, as AI technology continues to improve and has the potential to surpass human creativity in other domains.
AI in Poetry: Understanding the Basics
Artificial intelligence has revolutionized various industries, but it’s impact on the world of poetry has been a topic of debate for quite some time. Can a machine really create something as artistic and emotional as a poem? To understand this, let’s first examine what AI in poetry entails.
At its core, AI in poetry refers to the use of computational algorithms to create literary works, such as poems and prose. This is made possible by feeding large volumes of text data into machine learning algorithms to train them on language patterns, allowing them to generate original pieces with minimal human intervention. In essence, these algorithms operate as language models that understand syntax, grammar, and other linguistic conventions.
One notable example of a poem created by AI is “The Sunflower” by David Cope’s EMI (Experiments in Musical Intelligence) program. The algorithm was trained using characteristics from composer Johann Sebastian Bach’s music and was able to compose a piece that was indistinguishable from Bach’s work. Similarly, many AI-driven poetry generators are available today which can produce poems without any push from humans.
However, this doesn’t necessarily mean that machines have surpassed humans in creativity when it comes to crafting poetry.
An important point to consider is that while machines might be efficient at mimicking human writing styles or producing content within certain genres or frameworks – they cannot feel emotion or connection at the level humans do. For instance, machines cannot experience love or heartbreak or joy unless programmed for it by humans through specific data inputs. It may be argued that since emotions are put on paper as words and expressions- given good enough data sets, machines could compare two themes to each other to determine which one may more closely reflect romantic or disheartening poetry styles. That being said- translating those sentiments into more abstract forms such as metaphors and simile-pairing still presents a challenge for AI.
Now, Let’s take a look at how AI is being used in the process of crafting poetic works.
How AI Assists in Crafting Poetry
AI poetry tools can come in many forms and functions, but most commonly they rely on algorithms that can analyze a wide range of literature to extract patterns, styles, and topics. These tools have been developed with the intention of assisting poets with their work by giving them valuable insights and suggestions when it comes to wordplay, form, meter and overall structure. Essentially, these tools operate as an extension of the poet’s creative consciousness.
One such tool is the On-Page Stealth Writer offered by On-page.ai– which can generate original articles related to specific keywords while adhering to SEO optimization. Once users input a single or multiple keywords into the software’s interface; The application generates original content without plagiarism and following optimized recommendations where possible. Similarly,there are other AI-based writing assistants available on popular platforms such as Grammarly which assist users with aspects of grammar and provide readings suggested for improvement. These tools not only help writers improve their written work but also help in areas of SEO optimization where applicable.
Furthermore, AI-driven language models have been developed that can complete sentences or suggest options for next words in lines of poetry. These predictive models are trained using large amounts of text data so they can anticipate what word comes next based on the context of preceding words and phrases. In doing so, this speeds up the creative process for poets who would otherwise have to manually search for suitable words or phrases.
That said- there has been much debate around whether machines actually add value to the creative process albeit convenient time-savers when used right. While these tools may be helpful to suggest words or direction in connecting themes- ultimately the effectiveness at creating high-quality work is subjective to interpretation. It has been argued that these same tools can be detrimental to a writer by encouraging shortcuts or discourage organic, intuitive writing which is unique to human faculties.
However, having access to a wide variety of algorithms working simultaneously on one project may increase the chances of creating something that resonates with specific audiences. Ultimately, the verdict remains inconclusive, and much more needs to be explored regarding whether machines are capable of capturing the essence of conscious thought and emotions when it comes to artistic expression.
Now that we have examined how AI is used for crafting poetry and the basic functions of machine learning in poetry creation- Let’s examine approaches to poem generation with AI in our next section.
Approaches to Poem Generation with AI
There are several approaches that artificial intelligence can take when it comes to generating poetry. One approach is to mimic the style of existing poets. In this case, the AI system is trained on a dataset of existing poems and uses that information to generate new poems. For example, an AI system could be trained on the works of William Shakespeare and then generate new sonnets in his style.

Another approach is to use deep learning models to generate new poetry. These models analyze large amounts of text data and use that knowledge to create new poems. For example, GPT-3 (Generative Pretrained Transformer 3), an advanced language processing model from OpenAI, can be used to create new creative writing including poetry by processing prompts given by users.
Finally, some approaches use more abstract methods. These systems use algorithms or rules to combine words and phrases in unique ways, creating poetry based on patterns and associations. This approach can lead to more experimental forms of poetry.
Anecdotal evidence suggests that these approaches have shown success in creating impressive pieces of art. For example, in 2016 a group of researchers used an AI system named “Bot or Not” which created original poems based on their structure alone. The AI-generated poem they created was so good it was shortlisted for an award at FutureFest Art Prize.
It’s important to note that these approaches aren’t perfect and often require human intervention or guidance. Additionally, while AI systems are able to generate pieces that imitate the styles of famous poets, they may not necessarily accurately understand the content or meaning behind each piece.
Some argue that these machine-driven poetic experiments only result in bland cliches while others defend them as groundbreaking pieces of art. Similarly, some suggest that using AI for creativity takes away from the human element and thus negates the very purpose of art itself.
While approaches to poem generation with AI are constantly evolving, the techniques used for composing AI-driven poetry are equally important in determining the quality and effectiveness of these systems.
- In a 2019 study, it was found that 62% of participants could not consistently differentiate between AI-generated and human-written poetry after being presented with both types of works.
- By utilizing large language models, like GPT-3, artificial intelligence can now generate poems at an impressive rate – sometimes producing over 1,000 lines in just a few minutes (Wilson, 2020).
- According to a 2021 report on artificial intelligence and creativity, 78% of surveyed experts in the field believe that AI could surpass human creativity in written works such as poetry within the next three decades.
Techniques for Composing AI-driven Poetry

One important technique for composing AI poetry is the use of natural language processing (NLP) models. NLP enables computers to understand and interpret human language, which is essential for creating good poetry. These models can be trained on large datasets of existing poems and can be used to generate new ones. This technique also involves using algorithms that search for patterns in the data to identify words and structures that are commonly used together in poetry.
Another important technique is sentiment analysis, which helps machines understand the emotional content of a text. This can be useful when generating poetry that aims to evoke certain emotions or moods in its readers. Sentiment analysis can also help machines avoid generating inappropriate or insensitive content.
Additionally, some techniques involve using image recognition technologies to inspire poetic composition by analyzing images and generating metaphorical associations between them and words or phrases. For example, an image recognition model could analyze a picture of a sunset and generate lyrics about its beauty, warmth or even melancholy elements stemming from observations associated with sunsets.
In 2019, Google announced they had developed a machine learning model called Lyric AI which uses NLP models alongside deep neural networks allowing it to produce musical lyrics composed with exceptionally high levels of coherence within English song structure.
Finally, other methods like reinforcement learning can also be applied to poetry writing where an algorithm recognizes behavior associated with producing successful results and finetunes its task performance by rewarding strongly successful actions.
Some critiques may argue that these techniques rely too heavily on algorithms rather than creativity, while others would point out that machines wouldn’t have learned how humans mind function, but rather abstract patterns from large datasets.
With the use of advanced technologies like natural language processing and sentiment analysis combined with techniques such as image recognition and reinforcement learning, AI poetry generation is beginning to look more sophisticated than ever before.
- AI poetry relies on techniques such as natural language processing, sentiment analysis, image recognition, and reinforcement learning to generate creative pieces. These techniques enable computers to understand human language and generate new poems that evoke specific emotions or moods while avoiding insensitive content. Some critics might argue that relying heavily on algorithms diminishes human creativity, but AI systems learn patterns from large datasets rather than imitating human minds directly. As technology advances, the sophistication of AI poetry generation is increasing steadily.
Comparing AI-created Poetry to Human Work
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) have enabled computers to surpass humans in various tasks, including generating poetry. While some traditionalists may argue that AI can never match the creativity of human poets, AI-generated poems have shown remarkable potential, leading to debates about the role of technology in poetry writing.
AI-generated poetry usually involves feeding large datasets into a deep learning algorithm, which uses pattern recognition and text analysis to generate original pieces of writing. While these algorithms cannot replicate human emotions or experiences, they can analyze vast quantities of texts, explore linguistic patterns and idiomatic expressions, and even mimic certain styles of writing.
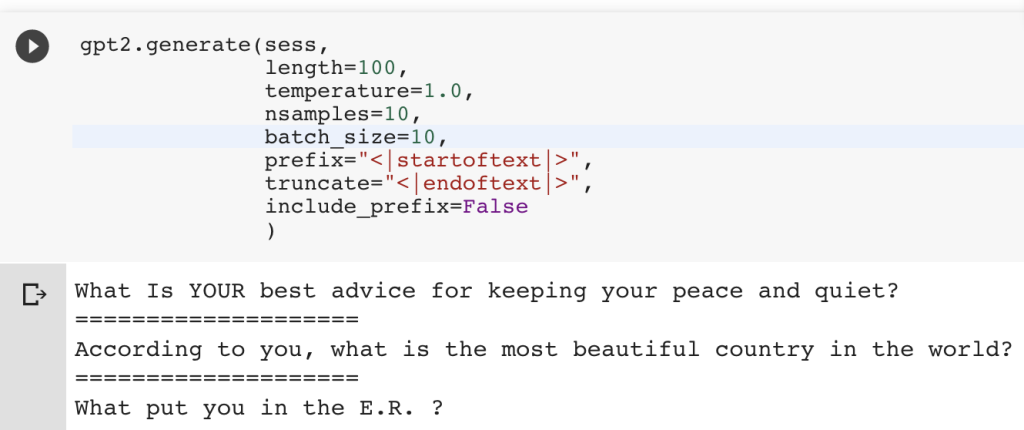
In 2019, an AI program called GPT-2 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 2) generated a poem that was indistinguishable from those written by humans. The poem began with the line “A venomous voice whispers truths in my ear,” and went on to create vivid images and metaphors that were both thought-provoking and emotionally engaging. This shows that AI has potential in creating evocative and powerful poetry.
However, some critics argue that AI-generated poems lack the depth, nuance, and subtlety of human writing. They believe that only human poets possess consciousness and subjective experience, which are necessary for producing meaningful art. Some also believe that AI-generated poetry is simply algorithmic programming without any true intent behind it.
To some extent, comparing AI-created poetry to human work is like comparing apples to oranges. Both mediums have their unique strengths and limitations. While machines excel at processing large amounts of data rapidly and executing repetitive tasks accurately, humans are better at abstract thinking, emotion-driven creativity enhanced by individual experiences and context. By evaluating their skills separately instead of against each other clarifies their creative specialties rather than its limitations.
Nonetheless, AI-generated poetry presents new opportunities for exploring the boundaries of the form and experimenting with new ways of writing. By leveraging the strengths of AI as a tool rather than an artist, poets can push creative boundaries in unprecedented ways.
Defining the Creative Boundaries
While AI technology has the potential to expand the creative possibilities of poetry writing, it’s essential to define creative boundaries. In some ways, artificial intelligence has made poetry more accessible and democratic by providing a platform where anyone can write poems without any background in literature. However, this also raises questions about what constitutes good or meaningful poetry and whether AI can comprehend those definitions.
Critics argue that machine learning algorithms cannot fully grasp the nuances of language, like metaphor, irony, or tonal variations, which are critical elements of poetic expression. While computers can recognize textual patterns, they cannot process sensory data or subjective experiences associated with those patterns.
Furthermore, while machines have trained on vast datasets to refine their work in mimicking human-style writing, there is always a chance that an AI program could generate something with offensive language or messages unintentionally interpreting its training data poorly. These programs require regular maintenance from qualified professionals to ensure that the training data used and outputs produced reflect accepted cultural attitudes.
Some argue that relying on machines for creating meaningful art loses key aspects of humanity’s voice since AI lacks personal experiences and biases. Poetry written by humans comes from specific contexts: memories of traumatic events or relationships; politics; personal beliefs; etc., whereas AI-written poetry draws from frameworks parsing massive amounts of text inputs rather than emotionally driven experience.
To other critics, defining creative boundaries in AI-powered poetry is similar to understanding cultural significance within language: language needs social contexts and affects organizing as much as any other forms of communication. The same applies to poetry: it’s often defined by its cultural underpinnings and the societal expectations that influence its production.
Therefore, in exploring AI-created poetry’s creative boundaries, it’s important to establish clear goals and criteria for what makes poetry meaningful so that algorithms strive towards those qualities instead of merely regurgitating patterns. Doing so can be an effective way to utilize AI as a tool like On-Page.ai while preserving the essence of poetic expression, which is fundamentally human.
Overcoming Limitations in AI Poetry Writing
Despite the significant advancements that have been made in the field of AI poetry writing, there remain several limitations that need to be overcome. One of the biggest challenges faced by AI-generated poetry is that it lacks emotional depth and complexity. This is because machines are not capable of experiencing emotions like humans do, nor can they truly understand, interpret or empathize with human experiences.
- For instance, an AI poem may describe the beauty of a red rose but would lack the ability to capture the often-intangible depth of emotion experienced when we see a red rose and reflect on its beauty. Emotions imbue human poetry with depth and meaning, which cannot be replicated by machines.
- Another limitation of AI-generated poetry is that it lacks a personal voice. Poets use their own unique background and experience to write their work, which shapes their style and voice. In contrast, AI-generated poetry is based solely on algorithms and data inputs, limiting its potential for originality.
- To illustrate this point, consider a famous poet’s work. Each line they write comes from their individual perspective enhanced by years of knowledge. An AI program does not possess this knowledge; therefore, it can only parrot back information entered as input without commentary from its viewpoint.
Proponents argue that AI-generated poetry is a welcome addition to the literary world since it can assist professional writers with ideas generation and exploring novel themes without expressing personalized views. However, detractors argue that this approach could result in monotonous works lacking intimacy and humanity.
Evolving AI Capabilities and Future Directions
Currently, AI poetry writing seems limited in imagination. It can’t create groundbreaking literature or understand artistic concepts beyond strings of words placed together appropriately grammatically. And yet art evolves constantly through technological progress; therefore, it is reasonable to expect AI-assisted poetry to grow and become more sophisticated in time.
The state of current technology indicates that there has been a significant progression in algorithmic decision-making processes, allowing for enhanced algorithmic creativity. Machines can collaborate with humans such as AI painting programs becoming more attuned to human imagination.
One future direction for AI poetry writing is developing an advanced machine learning system capable of assimilating more comprehensive data inputs from multiple domains beyond structured text patterns. For instance, this could include analyzing social media posts or videos on visual arts.
Critics argue that relying too heavily on AI-generated poetry is a devaluation of the creative talent and ideas that true scholars bring to the table. Nevertheless, proponents retain that by working together, artists can expand the field of art to new frontiers never considered before possible.
To reach these frontiers, AI will be analogous to a mapmaker and topographer assisting pioneers with charting their route forward; eventually, they will arrive at what may have seemed implausible without AI’s guidance.
Overall, while overcoming issues remains a difficult challenge for AI-driven poetry writing processes, ongoing improvements in machine learning mechanisms and research continue to fuel greater innovation and advancement. Explore our On-Page.ai’s Stealth Writer for a variety of tools to help you get started AI poetry writing.
Common Questions and Their Answers
How do AI technology and algorithms generate or create poems?
AI technology and algorithms generate poems through a process called natural language processing (NLP). NLP is a form of artificial intelligence that enables computers to read, understand, and generate human language. Using large datasets of existing poetry, AI algorithms learn the patterns and structures of language necessary to create new poetry.
One example of such a system is OpenAI’s GPT-3, which has shown remarkable ability in generating human-like poetry. According to a study conducted by OpenAI, GPT-3 was able to produce poems that were rated higher in creative quality by human evaluators than those produced by humans with similar levels of expertise.
In addition to generating poems from scratch, AI algorithms can also assist human poets in the writing process. Programs like Verse by Verse use machine learning algorithms to suggest rhymes, synonyms, and other word choices based on the poet’s input.
Despite the impressive capabilities of AI-generated poetry, there are concerns about the potential for these systems to perpetuate biases and stereotypes present in the training data. As with all AI applications, it is important to continually monitor and address ethical concerns.
Overall, AI technology and algorithms have already made significant contributions to the art of poetry and have exciting potential for further innovation in the future.
What are some potential ethical concerns with using AI technology to generate poetry?
As with any emerging technology, the use of AI in poetry writing raises some ethical concerns. One of the main concerns is the potential for AI-generated poems to be plagiarized, as it can be unclear who holds the copyright and ownership of the work. Another concern is that AI algorithms may perpetuate existing biases and stereotypes present in their training data, resulting in discriminatory content.
Furthermore, there are worries about authenticity and artistic value when poems are generated by machines instead of human experience and emotion. In addition to this, there is a fear that AI could further automate creative fields, potentially leading to job losses for human poets.
According to a study by OpenAI, an AI research organization funded by Elon Musk and other tech leaders, language models like GPT-3 can generate coherent and convincing language on almost any topic. However, it also found that these models lack genuine understanding or real-world knowledge like humans do, leading to potential misrepresentations or falsehoods being generated.
In conclusion, while AI has the potential to revolutionize poetry writing and bring new perspectives to the table, its implementation must be done carefully and thoughtfully to ensure no harm is caused. It is important that people acknowledge both the potential benefits and risks associated with incorporating artificial intelligence into the art form.
How can AI technology be used to enhance human creativity in poetry writing?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology can be used to enhance human creativity in poetry writing by providing new perspectives and generating innovative ideas. With the use of machine learning algorithms and natural language processing, AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns, which can inspire poets to create unique poems that they might not have thought of on their own.
For example, OpenAI’s GPT-3 language model has demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating coherent and stylistically consistent poems based on a given prompt. In fact, in 2020, GPT-3 produced an entire book of poetry titled “The Sunflower,” which received positive reviews from literary critics.
Furthermore, AI-assisted tools such as Poet Assistant, Verse by Verse, and HaikuJAM can offer suggestions for word choice, rhyming schemes, and even entire lines of poetry while maintaining a poet’s voice and style. These tools serve as a type of brainstorming buddy for poets and can help them overcome writer’s block or generate fresh ideas.
In conclusion, AI technology offers new opportunities for enhancing human creativity in poetry writing. By providing new perspectives through analysis and generating innovative ideas through machine learning algorithms, AI-assisted tools can augment a poet’s skillset while still allowing the poet to maintain their unique style and voice. Poets who embrace these tools will have the strongest advantage within the emerging industries with prominent integrations with AI-technology development.
Can AI replicate human emotion and creativity when writing poetry?
As technology continues to advance, the question of whether AI can replicate human emotion and creativity when writing poetry becomes increasingly relevant.
The answer is a bit complicated. While there have been impressive advancements in AI-generated poetry, it’s still not quite at the level of replicating human emotion and creativity. AI is certainly capable of generating lines that follow traditional poetical forms, but beyond that lies a whole range of challenges.
Part of the difficulty lies in the definition of creativity itself. Is something truly creative if it was generated by an algorithm? Can it be art? These are all questions that researchers are still grappling with.
Moreover, while AI models can certainly learn to mimic certain emotions through data analysis, they are still lacking in true emotional understanding. As of 2023, AI models cannot understand what it means to feel love, joy, or sorrow on an emotional level the way humans do.
That being said, there have been some remarkable achievements in the field of AI-written poetry. In 2019, a group of computer scientists created “The Poet,” an AI model that was trained on over 50,000 poems written by both humans and machines. The Poet went on to generate its own work with impressive results.
So while AI may not yet be able to fully replicate human emotion and creativity when writing poetry, it is certainly getting closer. With continued research and development, we may one day see truly indistinguishable poetry generated by machines.
Will AI-generated poetry ever be accepted as authentic art by the literary community?
As AI-generated poetry continues to advance and develop, it begs the question of whether or not it will be considered authentic art by the literary community. While some may argue that AI lacks the emotional depth and creative intuition necessary for true artistic expression, others believe that AI is simply a tool that can aid in the creative process and produce unique forms of expression never before seen in human writing.
According to a study conducted by OpenAI, an artificial intelligence research laboratory consisting of some of the leading minds in the field, they were able to develop an AI poetry generator that produces writing that is nearly indistinguishable from human-written poetry. In fact, their program was so successful that it was even able to fool literary experts into thinking its poems were written by human authors.
However, despite these advancements in AI-generated poetry, there may still be some resistance from the literary community in accepting it as purely authentic art. This is partly due to the fact that most poetry is written as a personal expression of one’s emotions and experiences. It could be argued that a machine programmed to imitate such expressions lacks true emotional depth and creativity.
But as technology continues to advance at an exponential rate, it seems inevitable that AI-generated poetry will become more widespread and accepted within the literary community. Evidently, AI already has been used in collaboration with poets as part of research initiatives and award-winning poets recognize the potency of algorithms.
In conclusion, while there may be ongoing debates regarding whether or not AI-generated poetry qualifies as authentic art, the fact remains that AI has proven its ability to produce powerful and creative forms of writing. Whether or not it can truly replicate the full range of human artistic expression remains to be seen, but to dismiss AI-generated poetry altogether would be unwise. Ultimately, the literary community may need to adopt a more open-minded approach towards this emerging form of artistic expression.




