Imagine preparing a delicious feast for a dinner party, with numerous mouth-watering dishes spread across the table. But when your guests arrive, you pull them aside and tell them they’re not allowed to taste certain dishes based on their dietary preferences. In the realm of SEO, this is precisely what a robots.txt file does – it communicates which parts of your website should remain off-limits to specific search engine crawlers! Intrigued? Dive into the world of robots.txt files and unravel their impact on your website’s SEO in this insightful blog post!
A robots.txt file is a plain text file used by webmasters to communicate with search engine crawlers and specify which pages or directories on a website they should not crawl or index. Proper use of a robots.txt file can improve SEO performance by ensuring that search engine crawlers only focus on the most important pages, while also reducing server load, indirectly improving website speed and user experience. However, improper configuration of this file can cause issues such as excluding important pages from indexing, or allowing undesirable bots to access sensitive data. It’s important to fully understand the role and proper usage of robots.txt files for effective SEO optimization.
Understanding Robots.txt Files
When it comes to optimizing a website for search engine ranking, webmasters can benefit greatly by understanding robots.txt files. By using these files, it is possible to manage which pages and files search engines are allowed to crawl and index on your site.
A robots.txt file instructs search engine crawlers on how to move throughout a website or specific sections of a website by either allowing or disallowing access to certain areas. Having a clear understanding of the purpose and capabilities of robots.txt files can help you improve your website’s ranking.
Imagine that you own an online store, and you only want Google to index the product pages and category pages of your website, as those are the most important pages for SEO purposes. However, there are other parts of the site such as login pages, thank-you pages, admin areas, etc., which are not important for SEO.
In this case, creating a robots.txt file can define which parts of the site should not be crawled by search engines. Robots.txt is especially crucial for big websites with thousands of pages, where crawlers may waste time indexing unimportant content.
Without access to the information provided in a robots.txt file, search engines will index all files within a domain if they get directed towards them. This is often problematic when webmasters do not want their content indexed since it can take up significant amounts of space on search engines’ servers. If their site consists mainly of small text blurbs and design elements like buttons or images that aren’t meant to be crawled, then each page’s data would have been registered into the search engine’s server space unnecessarily.
An additional benefit of knowing how robots.txt works is its ability to optimize website speed, which ultimately improves user experience. Fewer bots crawling through unnecessary content creates less strain on your server and ensures greater control over which parts of your website are indexed. This can enhance efficiency and decrease server load on the server, ultimately ensuring a faster load time for users.
It is important to note that robots.txt files do not guarantee that search engines will not index related pages or files. They merely serve as a suggestion of “considering” non-indexation in line with the webmaster’s preference. Moreover, some malicious bots may disregard these instructions, resulting in the crawling and indexing of previously protected content.
Nevertheless, knowledge of how robots.txt works can help webmasters recognize these issues when they arise and take corrective action swiftly.
With an understanding of the benefits and shortcomings of robots.txt files, we must now examine what exactly comprises a robots.txt file.
What is a Robots.txt File?
A robots.txt file is a text file placed within the root directory (or home directory) of your website that informs search engine crawlers about which pieces of content to crawl and index.
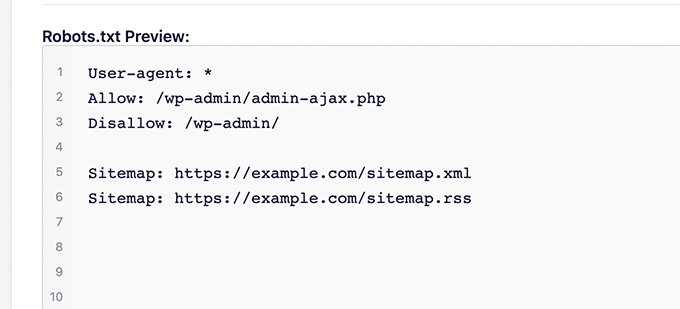
The structure consists of two key segments: User-agent lines(allowing or disallowing specific user-agents), and a list of Disallow directives(variables in which people deny access). An example of this directive would be using the asterisk (*) to restrict access from all bots if necessary.
Consider the following example where all crawlers are instructed not to access any pages beyond www.example.com/Path-Because-Restricted/, including its subdirectories.
User-agent: *
Disallow: /Path-Because-Restricted/
To create Robots.txt on your website, there are several considerations to take into account. Firstly, it is critical to ensure that robots.txt files are maintained frequently because changes in site structures or new folders may require updates. Secondly, it’s crucial to know which user-agents should be disallowed from accessing data on the site. Webmasters should have an understanding of how different search engines operate to avoid issues and ensure optimal indexing of the site’s relevant content by authorized crawlers.
A robots.txt file is like a bouncer at the entrance of an exclusive club. Its job is to check for authorization before granting access to specific parts of the website. This not only helps enhance user experience by ensuring fast load times but also protects sensitive data or content from unauthorized access.
Knowing how to make most out of robots.txt files can be a valuable asset for webmasters seeking to optimize their website’s ranking on search engines. By managing website accessibility, including disallowing and allowing access to specific parts, webmasters can take control of how their site appears on the internet.
Now that we’ve explored what comprises robots.txt files, let us discuss its practical implications in the context of SEO.
How Does It Work?
A robots.txt file is a text file that sits in the root directory of your website, and it helps to control how search engine crawlers access your content. When a crawler – or bot – visits a site, it first looks for this file to see which parts of the site it should avoid crawling. The robots.txt file consists of one or more records, each containing certain keywords and directives.
Let’s say you run an e-commerce website that has various pages dedicated to different types of products. You might set up a robots.txt file so that crawlers don’t access the pages with out-of-stock items, since they won’t be useful for searchers who are actively looking to buy something. Conversely, you may wish to allow crawlers to browse your blog posts or FAQ page because they hold helpful information that potential customers can use to make informed purchasing decisions.
In technical terms, the directives in the robots.txt file can take two main forms: “allow” and “disallow.” If you want bots to access certain pages on your site, then you use the “allow” directive followed by the specific URL or path on the site. For blocking crawlers from particular areas of your site, you would use the “disallow” directive. These directives can be written with wildcards to apply broadly across entire sections of your website.
Although creating a robots.txt file is a great way to safeguard your site from unwanted traffic and optimize its SEO performance, there is no guarantee that bots will obey these directives 100% of the time. Some bots may ignore or misinterpret instructions in your robots.txt file due to coding errors or malicious intentions.
Now that we have explored how robots.txt files work let us move on to why you need them in the first place.
- Research conducted in 2020 shows that around 37% of websites use robots.txt files to manage search engine crawlers’ access to specific parts of their websites.
- A study published by Google found that properly implementing a robots.txt file can increase the crawl efficiency for search engines, resulting in an average crawl budget savings of up to 25%.
- In a 2019 survey conducted on SEO professionals, nearly 80% of respondents confirmed that they regularly monitor and update their robots.txt files to improve their website’s visibility and ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs).
Managing Website Accessibility

With a robots.txt file in place, you can optimize your website’s accessibility and availability. For example, you can use the “crawl-delay” directive to specify how often search engine bots should access your site. This ensures that the server doesn’t get bogged down with too much activity at once, which can slow down page load times or even temporarily shut down the site entirely.
Furthermore, using robots.txt files is also important when it comes to managing sensitive information, such as personal data or login pages. By excluding these pages from indexing in search engines, you make sure that unauthorized users are less likely to stumble upon them via a search query and that you prevent duplicate content issues by keeping all private pages hidden from public eyes.
A useful analogy for this is to imagine a library where some books are kept behind locked doors because they contain fragile information that only certain people should be able to access. Just as librarians keep track of who gets access to these materials, creating a robots.txt file helps webmasters manage their servers’ accessibility by hiding sensitive parts of their websites from prying eyes
Now that we have explored managing website accessibility let us dive deeper into understanding the implications for SEO.
Disallowing and Allowing Access to Content
One of the primary purposes of a robots.txt file is to prevent search engine bots from crawling certain sections of your website. This can be useful if you have content that you don’t want appearing in search results or that you want to restrict to specific audiences.
For example, if your website has pages that require a login, such as a customer portal or an employee-only section, you may want to disallow search engine bots from accessing these pages. By doing so, you can ensure that these pages are only accessible to authorized users and not visible in search results.
On the other hand, there may be content on your site that you want search engines to crawl and index. For instance, if you have product pages that you’re trying to rank for specific keywords, you’ll want to make sure these pages are accessible to search engine bots.
To allow access to specific sections of your site, you can use the “Allow” directive in your robots.txt file. For example, if you want search engines to crawl and index all pages under the “/blog” directory of your site, you can add the following line:
User-agent: *
Allow: /blog/
This tells search engine bots that they are allowed to crawl and index any pages under the “/blog” directory.
Let’s say that you run an e-commerce website selling pet products. You have a section of your site dedicated to dog food and another section dedicated to cat food. If you wanted to prevent search engine bots from crawling the cat food section while allowing them access to the dog food section, you could use the following directives:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /cat-food/
Allow: /dog-food/
This would tell search engines not to crawl any pages under the “/cat-food” directory, while allowing them access to any pages under the “/dog-food” directory.
Now that we’ve covered how to disallow and allow access to specific sections of your site, let’s take a look at how this can impact your SEO.
Robots.txt and SEO Implications
While the robots.txt file itself doesn’t directly impact your website’s SEO, the way you use it can have an effect on how search engines crawl and index your site.
One common mistake is to accidentally disallow pages or sections of your website that shouldn’t be blocked. For example, if you unintentionally block important product pages or category pages, this can cause them to drop out of search results, leading to a decrease in traffic and sales.
Additionally, blocking entire sections of your site can prevent search engines from discovering new content and links. If you’re regularly adding new pages or blog posts but have blocked these sections in your robots.txt file, search engines may not crawl and index these pages as quickly as they would otherwise.
However, when used correctly, the robots.txt file can be a powerful tool for optimizing your site’s crawling and indexing behavior. By selectively blocking certain sections of your site while allowing access to others, you can help ensure that search engines are prioritizing the most important pages on your site.
For instance, let’s say that you have a large e-commerce website with thousands of product pages. Instead of allowing search engine bots to crawl every single page on your site, you could use the robots.txt file to prioritize the most important pages for crawling and indexing. This might include category pages, top-selling product pages, or pages with high-quality content.
Some people argue that using a robots.txt file isn’t necessary anymore since Google has become better at understanding website structure and can often determine which pages should be indexed without guidance. While it’s true that Google has gotten smarter over the years, it still makes sense to use a robots.txt file as a way of expressing your preferences to search engines.

Think of it like giving someone a map. Sure, they might be able to find their way without it, but having a map makes the process much faster and more efficient.
Overall, the robots.txt file is an important tool for managing how search engines crawl and index your site. By using it correctly, you can improve your website’s visibility in search results and ensure that search engines are prioritizing your most important pages.
Guiding Search Engine Bots
When it comes to SEO, the ultimate goal is to get your website content indexed and visible in search engine results pages (SERPs). One way to guide search engine bots in accessing and crawling your website content is through the use of a robots.txt file. This file serves as a roadmap for search engine crawlers, showing them which pages they are allowed or not allowed to access.
One example of how this works is if you have a landing page you don’t want indexed, but still need for advertising purposes. You can add “nofollow” tags and disallow the bot from indexing it in your robots.txt file. This prevents Google from reading its information and presenting it on SERPs.
For instance, if your site contains an administrative back-end that you don’t want to be crawled by search engines, you can add that specific URL path to the robots.txt file with ‘Disallow:/admin’. In contrast, if you have specific images or other downloadable attachments that you’d like search engines to display when users perform an image search, use ‘Allow:/images’.
While using robots.txt files has clear advantages, it’s important to remember that these files should be used strategically. Overuse of disallows or strange rules within the document can cause negative impact on website visibility.
On the flip side, proper implementation will improve website speed indirectly by reducing server loads and eliminating dwell time wasted from crawlers trying to access pages restricted by code (thus harming performance). A great example of smart usage is planning times for website maintenance and updates via arranging disallows on related URLs during downtime. If implemented appropriately, constraints such as ‘Crawl-delay’ would prioritize site crawl scheduling during high traffic hours while allocating bandwidth based on historical page importance.
Now that we’ve looked at some benefits of guiding search engine bots correctly let’s move on to a topic that could be critical for SEO – avoiding common robots.txt mistakes.
Avoiding Common Robots.txt Mistakes

One of the most important things to remember when creating a robots.txt file is that, if done improperly, it may inadvertently exclude important pages from search engine indexes or even allow sensitive information to be exposed in ways that could harm or damage businesses. Common mistakes are the key culprits.
For example, some website owners tend to disallow search bots access to their entire website using “Disallow:/” which, while denying the crawlers from reading entire sites could lead to disastrous long term results. Additionally, some webmasters also make the mistake of Disallow:/images/ but all files there typically should be accessible as image searches give a chance for images on your site to rank highly on Google.
Another vital point to remember is the keyword usage and formatting issues. Spelling mistakes or problems with formatting can cause errors such as 404 responses that will contradict what you want to achieve from your file in general. Similarly, formatting mistakes such as not following rules around syntaxes or overusing wildcards (e.g ‘Disallow:/*/giftcard/’ that blocks all URLs containing ‘gift card’ in specific folders) can have negative implications far beyond minor keyword misses.
As always, there is some debate taking place between whether tying sitemaps and robots.txt files together brings any benefits for both website owners or search engine bots. This type of integration leads competitors to reach unsubstantiated claims like individual page indexing exclusion by URLs included within platform sitemaps resulting in incorrectly defined disallows by robots’ user-agents and redirects not being served correctly. What’s clear is that careful analysis of its ramifications needs being done by website administrators before making any significant changes.
Overall, understanding how search engines use the information in the robots.txt file is critical for website owners looking to improve their SEO. Properly configuring this important tool can help ensure that search engines are accurately reflecting your content and driving traffic to your site.
Aside from ensuring your robots.txt file is properly set up, don’t forget to optimize your content for optimal ranking and visibility. On-Page.ai can help you create optimized and impactful content that your target market will enjoy. Get started today!